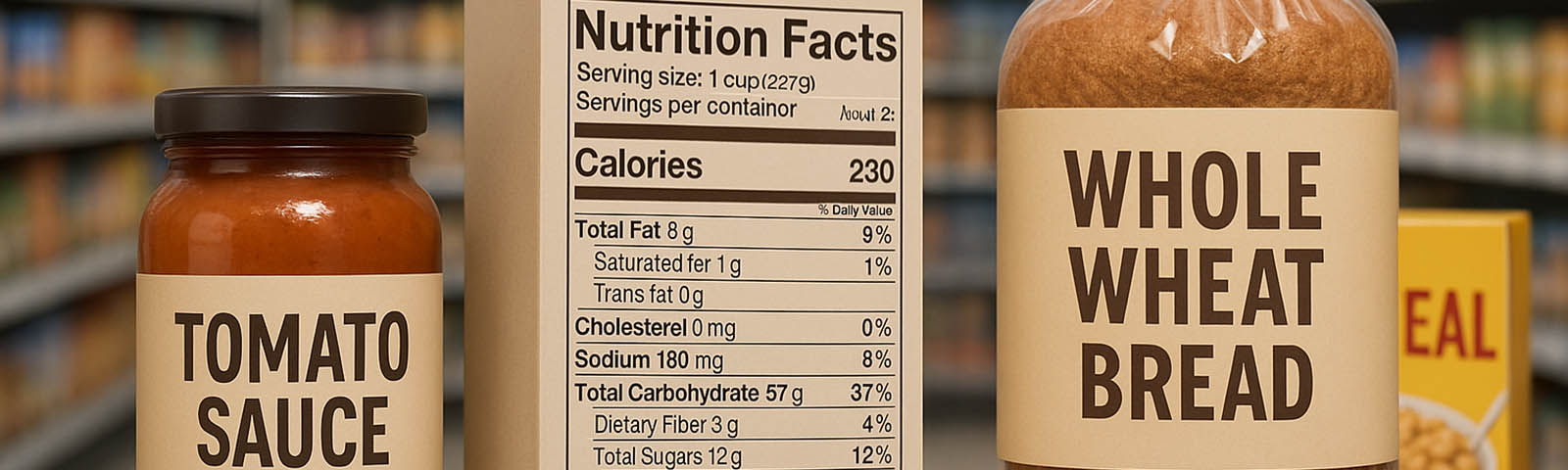
Earlier this week, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) took a significant step forward in regulating dietary supplements. The agency released a final guidance entitled “Dietary Supplements: New Dietary Ingredient Notification Procedures and Timeframes: Guidance for Industry.” This pivotal document aims to streamline the process for manufacturers and distributors of new dietary ingredients (NDIs) and dietary supplements, providing a clear pathway for submitting new dietary ingredient notifications (NDINs) to the FDA.
The new guidance is structured in a question-and-answer format, designed to address the intricacies of the NDIN submission and review process comprehensively. Among the key questions tackled are who is required to submit an NDIN, how to organize and present the necessary information, where to submit the NDIN and what steps to follow after the submission.
This structured approach ensures that industry stakeholders have a thorough understanding of the requirements and procedures, promoting compliance and safety in the dietary supplement market.
XTALKS WEBINAR: Nutritional Wellness for Women: Natural Solutions for Every Life Stage
Live and On-Demand: Tuesday, April 23, 2024, at 9am EDT (3pm CEST/EU-Central)
Register for this free webinar to learn about the science-backed ingredients and functional concepts that can support women at every life stage, including probiotics, vitamins and minerals.
The FDA’s NDIN Guidance
This guidance finalizes Section V (“NDI Notification Procedures and Timeframes“) of the 2016 revised draft guidance, along with several related questions from other sections of the draft guidance. The FDA’s decision to finalize these sections responds to feedback received on the draft and demonstrates the agency’s commitment to clarity and usability for industry stakeholders. The segmented approach allows for easier navigation of the guidance, enabling manufacturers and distributors to focus on the sections most relevant to their needs.
The importance of this guidance cannot be overstated. By clarifying the procedures and timeframes for NDIN submissions, the FDA aims to ensure that NDIs entering the market are safe and that consumers have access to reliable information about the supplements they choose. The guidance reflects the FDA’s ongoing effort to provide comprehensive oversight of the dietary supplement industry, a sector that has grown exponentially in both size and complexity over the years.
Manufacturers and distributors of dietary supplements and NDIs are encouraged to carefully review the final guidance. It is an essential resource for understanding how to comply with federal regulations concerning NDINs, ultimately contributing to the safety and efficacy of dietary supplements available to consumers.
A “Major Disappointment” According to Some
The Natural Products Association (NPA) expressed significant dissatisfaction with the FDA’s guidance, describing it as “a major disappointment” and akin to a “giant nothingburger.” According to the NPA, the guidance falls short of addressing critical concerns. This final guidance originates from draft versions that date back to July 2011.
Daniel Fabricant, president and CEO of the NPA, criticized the guidance for not adequately serving the needs of consumer safety, industry innovation or the regulatory framework. He argued that the guidance fails to deliver on its promises, leaving numerous important questions unanswered and potentially undermining the value of the NDIN process.
Despite the FDA issuing two draft guidances intended to guide potential submitters on the content and format of NDINs, Fabricant pointed out that the feedback from over 7,000 comments on the 2011 guidance appeared to be overlooked in the 2016 draft. The lack of substantial updates in the 2016 guidance led to an additional 700 comments, yet the agency has yet to make decisive moves to address the core issues that matter the most to consumers and the market.
In light of this perceived inaction, the NPA has vowed to persist in urging the FDA to establish a concrete strategy for enforcing NDIN guidelines domestically. Fabricant highlighted a concerning practice where companies bypass submitting an NDIN for their ingredients by leveraging the efforts and investments of others who have already completed the process. This “piggybacking” practice, as he described it, compromises the FDA’s ability to review manufacturing processes and product specifications, posing significant safety concerns.
The FDA’s final guidance on NDIN procedures and timeframes marks an advancement in the regulatory framework governing dietary supplements but still falls short according to critics like the NPA. As the FDA continues to review and finalize other parts of the 2016 revised draft guidance, stakeholders are encouraged to stay engaged and contribute to the ongoing dialogue surrounding dietary supplement regulation.
If you want your company to be featured on Xtalks.com, please email [email protected].










Join or login to leave a comment
JOIN LOGIN