Overcoming the challenges of plant protein application
The use of alternative protein offers a perfect solution to a more sustainable food production system. Customers are ready to embrace this trend, but will only do so if taste, texture and health remain uncompromised. Can we meet their expectations?
Ever-increasing customer expectations
The world population keeps increasing: in 2050, there will be nearly 10 billion mouths to feed. Our current animal food production system will not suffice. Therefore, food producers, ingredient companies and researchers are on a quest to find sustainable alternatives. Enter plant proteins. Available in abundance, they are often a side or waste-stream of existing food production processes. Moreover, they can offer additional benefits, tailoring to customer expectations regarding muscle health, improved digestion and weight control.
But while consumers are actively trying to eat more plant-based foods (and reduce their meat consumption), they are not willing to compromise on taste and texture. Indeed, customers’ expectations are sky-rocketing: they want something special, and they want it now. And it should be as transparent and sustainable as possible.
Bridging the gap
If we are to meet their expectations, we will need to bridge the gap between our understanding of animal-derived proteins and alternative ones, such as plants, algae and insects. Microalgae, for instance, are known to be highly functional as a foaming agent or emulsifier. But how to apply them without creating the infamous fishy and musty off-flavours, or their green or red off-colours? We could make use of insects. After all, they can quickly produce large amounts of protein-rich biomass and have the potential to convert low-value waste into higher-value insect proteins. But as long as the Western world struggles to accept their application in a visible form, we will need to grind them, leading to brown off-colouring and protein hydrolysis.
A success story of alternative proteins is presented by the extraction of RuBisCo, the world’s most abundant protein. NIZO scientists have been able to prevent off-colour and solubility issues while upscaling and testing the process at a semi-industrial level.
Selecting proteins
When it comes to meeting customer demands about muscle health and weight control, it pays off to look into the satiety potentials of various proteins. Whey protein, for instance, hardly increases in viscosity in the stomach. It is also easily degraded thus readily available for consumption, making it ideal for rapid muscle recovery. Casein, on the other hand, is broken down slowly and absorbed later, making it more ideal for long-term recovery. Pea protein takes a middle position, breaking down more quickly than casein, but slower than whey (fig 1).
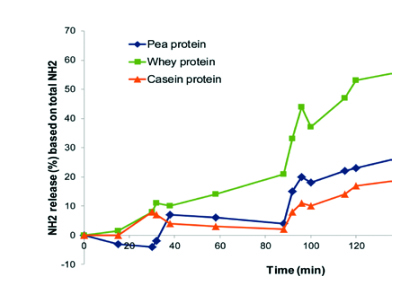
Solving taste and texture issues
Another issue we face is the deterioration of flavour and the decrease of solubility during extraction and processing. Increasing our understanding of their impact on the quality and functionality of proteins will enable us to adjust the production process and develop ingredients that deliver the optimal sensory perception. It is worth noting that we don’t need new and expensive drying techniques to keep plant protein in its native state. By adapting critical conventional steps during extraction and spray drying, it is possible to maintain functional properties and tailor ingredients for specific applications. For instance, by producing fibrillar structures from soy and pea protein isolates, NIZO was able to develop a meat alternative that delivered the bite and juiciness customers require from a meat product.
“By producing fibrillar structures from soy and pea protein isolates, a meat alternative was developed that delivered the required bite and juiciness.”
Blending proteins
If we are to live up to customer expectations concerning nutritional benefits, we will need to look into protein blends. After all, many plant proteins require blending to provide a complete nutritional profile. There are various tools on the market that support the search for the right proteins to be blended (fig 2).
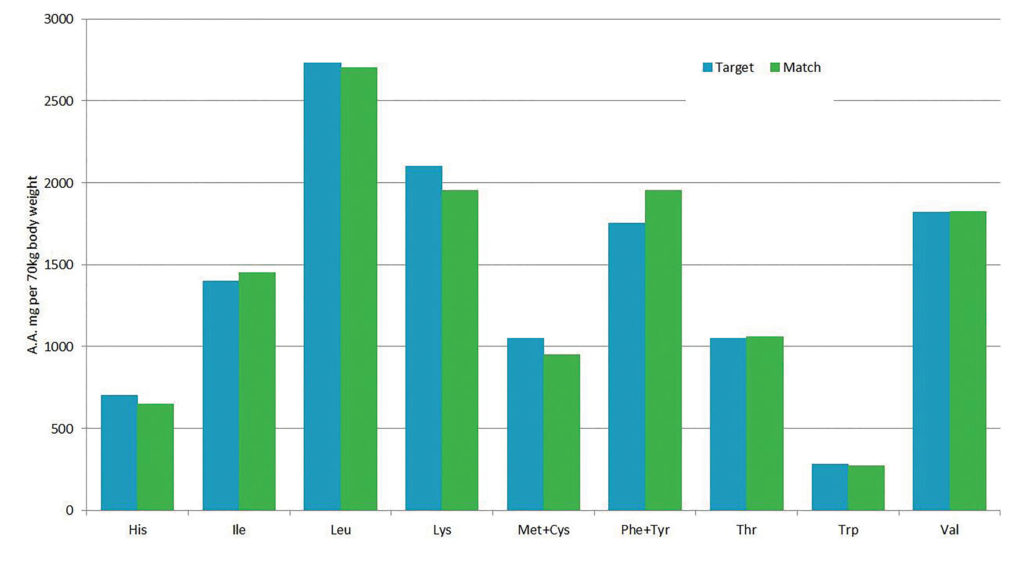
To tailor to customers who wish to experience new food sensations, we can use protein blends to develop food products with novel texture and sensory attributes.
Processing proteins
A final challenge to overcome has to do with the impact of product properties on processing conditions. For example, an important issue of spray drying is fouling of the dryer, due to stickiness of the product. This is especially true for products with a high content of carbohydrates and proteins, such as infant formula. Fouling results in shorter run times between cleaning procedures and at worst causes blocking of the dryer by lumps of powder. Improved process control by humidity measurements can minimise fouling, extend the time between CIP’s and avoid blockages.
Can we meet customer demand?
At the start of this article, we asked if we could meet customer expectations regarding flavour, texture, health and sustainability of plant-based products. The answer is: yes. But there are challenges to overcome.
Most importantly, we will need to expand our understanding of plant, insect and microalgal proteins. In addition, we can develop products with new texture and sensory attributes, or ensure that replacement of animal protein does not compromise taste, texture and nutritional properties. Either way, we will need focus on the creation of synergising protein blends and the optimisation of extraction and processing methods. Although we still have ground to cover, if we continue our quest, we will be able to feed those 10 billion people in 2050 with healthy, sustainable and tasty foods.
To learn more, register for Nizo’s upcoming webinar on Tuesday, October 29, 2019 here.
This article was created in collaboration with the sponsoring company and the Xtalks editorial team.
NIZO is the world’s leading company in contract research for better food and health. NIZO helps food companies to develop new tasty products by being able to understand, apply NPD development from fundamental scientific research all the way to the end product. NIZO, is the independent protein expert that makes your protein challenges become reality by developing tasty, multi-protein products. With deep knowledge in both animal (e.g. dairy) and plant proteins, we offer multi-disciplinary experience around the whole innovation pipeline as we understand how each development step is interrelated to the entire development process.











Join or login to leave a comment
JOIN LOGIN