The global biologics market is experiencing significant growth, projected to reach $732.4 billion by 2030, up from $421.1 billion in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2%. This surge underscores the increasing demand for efficient, cost-effective manufacturing processes, particularly in early-phase clinical programs.
As biologics developers accelerate timelines for first-in-human (FIH) clinical programs, the need for streamlined, flexible downstream processes is intensifying. For contract research, development and manufacturing organizations (CRDMOs), this means rethinking legacy purification platforms that may no longer meet the demands of early-phase production.
In a recent webinar, Indraneel Sanyal, Senior Director of Process Development at Aragen, detailed how the company adapted its monoclonal antibody (mAb) purification platform by transitioning from traditional resin-based Protein A chromatography to a membrane-based format. This shift, tailored for FIH biologics development, aims to lower upfront costs, enable quicker turnaround, and support scalable GMP operations — all while preserving product quality.
Below, we explore the key takeaways from the session and how Aragen’s adoption of membrane-based Protein A chromatography is advancing early-stage biologics manufacturing.
Resin-Based vs. Membrane-Based Protein A Chromatography in FIH Programs
Protein A chromatography is a widely used technique for mAb purification. Traditionally, this process has relied on resin-based formats, which remain effective at scale but introduce key inefficiencies in FIH clinical programs.
In the webinar, Sanyal outlined several challenges with using Protein A resins in early-phase manufacturing:
- High upfront resin costs, especially when only a small number of cycles are needed
- Inefficient utilization of resin lifespan, with the majority of cycles going unused in FIH scenarios
- Significant labor and time requirements for column packing and cleaning validation
- Increased plant occupancy, due to longer cycle times, cleaning steps and changeovers
- Dividing Protein A resin into several sublots for small batches increases post-harvest hold time, which may compromise the stability of the mAb
“It’s important to recognize that in early-phase work, if we only use about 10% of the resin’s useful life and the remaining 90% sits unused, the cost of maintaining that idle inventory becomes significant — and that cost ends up being spread across just a few cycles,” explained Sanyal.
To address this inefficiency, Aragen re-engineered its mAb platform to incorporate Protein A membrane chromatography — a ready-to-use, scalable technology aligned with the GMP demands of early-stage biologics.
Building a More Agile and Cost-Effective mAb Platform
In rethinking its mAb purification strategy for FIH programs, Aragen’s process development team set out to address the core limitations of resin-based Protein A chromatography — particularly in early-phase clinical settings where batch sizes are small and timelines are compressed.
The team identified three primary goals:
- Reduce upfront resin-related costs, which are often disproportionate in early-phase work due to limited resin reuse
- Maintain or improve productivity and purification performance, ensuring comparable product quality and yield
- Increase operational agility by minimizing labor-intensive steps like column packing and enabling faster batch transitions using plug-and-play membrane formats
These objectives are especially relevant in a CRDMO environment, where multiproduct manufacturing lines must remain flexible and compliant while meeting compressed clinical timelines.
Membrane-Based Protein A Chromatography: Performance and Reusability
As part of its platform transition, Aragen evaluated the performance of Protein A membrane chromatography across 60 consecutive cycles to assess its durability and suitability for FIH biologics manufacturing. The results demonstrated strong consistency and robustness:
- Host cell protein (HCP) and residual Protein A levels remained stable across all cycles
- Elution volumes and membrane backpressure showed no significant variation, even with repeated use
- Dynamic binding capacity (DBC) of 50 mg/mL was achieved at a 12-second residence time, balancing high throughput with process stability
Aragen optimized the operating conditions to achieve a 13-minute run time per cycle, using 90 membrane volumes, enabling efficient mAb capture without the extended run durations typically associated with resin-based columns.
Initial performance validation confirmed the membrane format’s ability to maintain output consistency across cycles — laying the groundwork for the cost and scalability modeling explored below.
Cost and Scalability Comparison: Membrane vs. Resin-Based Protein A Chromatography
To evaluate the operational and economic advantages of transitioning from resin-based to membrane-based Protein A chromatography, Aragen used the Sartorius Expert Chromatography Intensifier Tool to model performance across four typical FIH manufacturing scenarios:
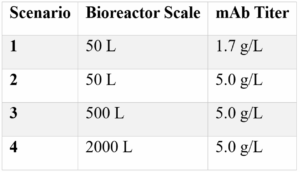
Each scenario compared key process metrics between resin-based and membrane-based formats, focusing on material costs, plant occupancy, buffer use and productivity.
Key outcomes of the membrane-based approach included:
- Up to 3x reduction in cost per gram of mAb in the capture step
- ~20-fold increase in productivity (measured in g/L/hr) compared to resin
- ~7-fold improvement in cost-efficiency (g/1,000€/hour)
- Lower plant occupancy due to shorter cycle times and reduced cleaning/changeover requirements
While membrane chromatography consumed more buffer volume per batch, this was outweighed by cost savings in resin, hardware and labor. The format also eliminated the need for resin packing and cleaning validation, further improving operational readiness.
These results underscore membrane chromatography’s suitability for FIH programs, where speed and cost-efficiency are essential but resin reuse is inherently limited.
Modernizing mAb Purification for FIH Biologics
By evolving its mAb purification platform from resin-based to membrane-based Protein A chromatography, Aragen has introduced a purpose-built solution for the realities of early-phase biologics manufacturing.
The transition delivers measurable benefits:
- Increased throughput through rapid, repeatable cycles
- Lower cost per gram of antibody at small scale
- Shortened facility occupancy with reduced operational overhead
- GMP readiness with flexibility across production scales
“The whole crux of the benefit lies in quick turnaround time… that’s the cost advantage,” Sanyal explained.
As Aragen continues to refine this platform through downstream intensification strategies, it reinforces its ability to support fast-moving clinical programs without compromising quality or compliance.
Watch the full webinar on-demand to explore how Aragen’s membrane-based approach is redefining mAb purification for FIH development.
This article was created in collaboration with the sponsoring company and the Xtalks editorial team.








Join or login to leave a comment
JOIN LOGIN