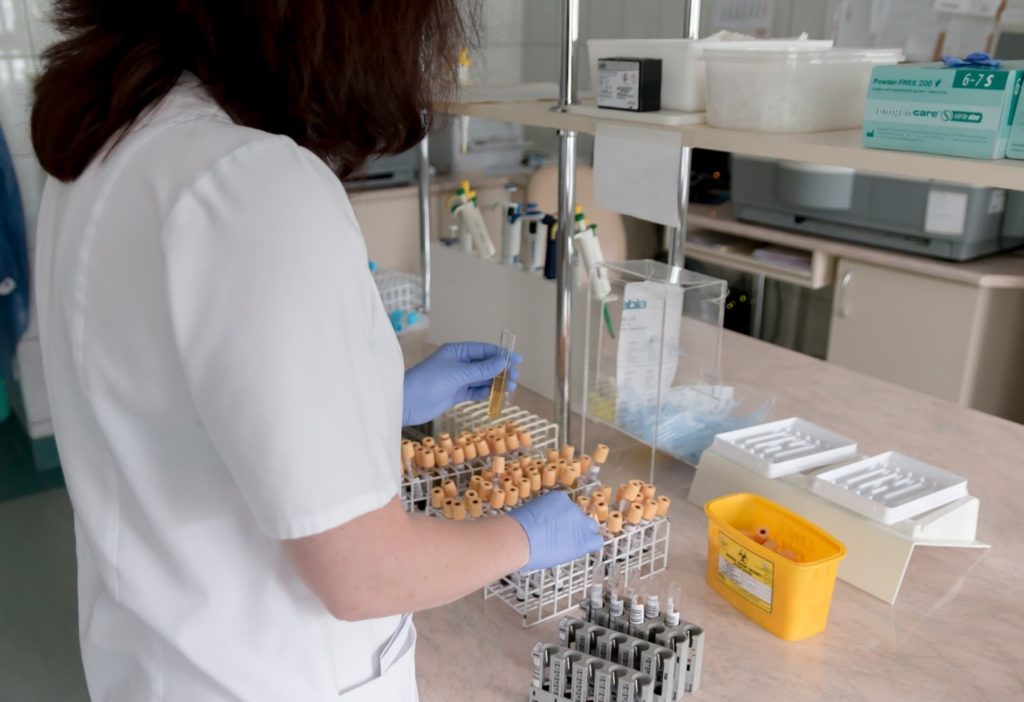
The Aptima CMV Quant Assay helps to detect changes in the viral load of the transplant patient to understand the response of the individual to anti-CMV treatment.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection in Transplant Recipients
The first successful organ transplant was a kidney transplant performed in the early 1950s. Data by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network indicates that 41,354 organ transplants were performed in the US in 2021, a 5.9 percent increase compared to 2020. The success rate of the transplant surgeries is increased by administering immunosuppressant (anti-rejection) medications.
Clinical immunosuppression drugs such as ciclosporin, tacrolimus, sirolimus, prednisone and everolimus are administered to the recovering recipients to prevent transplant rejection. When a person is under immunosuppression therapy, they are prone to get infected by a ubiquitous herpes virus called cytomegalovirus (CMV). CMV infection strongly influences the increase of morbidity and mortality in transplant recipients. The most prevalent methods of diagnosing CMV infection are PCR amplification and the pp65 antigenemia assay that detects the presence of CMV antigen pp65.
While in adulthood, 60 to 100 percent of people are infected by CMV, and an immunocompetent host may be asymptomatic, have mild symptoms or in rare instances the infection can result in a systemic syndrome.
The life of the transplant recipient crucially depends on the early detection of any signs of organ or graft rejection. CMV infection in transplant recipients is a common complication. In immunocompromised patients, the incidence of CMV infection in heart and lung transplant recipients is 50 to 75 percent, whereas in kidney transplant recipients it is approximately 50 percent. The detection of CMV infection during the preliminary infection period is vital.
The Aptima CMV Quant Assay — Efficacy and Reliability
On Tuesday, the Aptima® CMV Quant Assay developed by Hologic Inc. received approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This diagnostic assay works on the principle of in vitro nucleic acid amplification using real-time transcription-mediated amplification (TMA) technology.
The Aptima CMV Quant Assay helps to detect changes in the viral load of the affected patient to understand the response of the individual to the anti-CMV treatment.
“It is imperative to have highly accurate, reproducible results to monitor viral load trends of CMV infections over time in plasma of transplant patients,” said Karen Harrington, PhD, Head of Scientific Affairs for Diagnostic Solutions at Hologic in the company’s recent press release.
To emphasize the reliability of the developed assay, Harrington also added, “Our assay aligns with the international quantitative standards, offering laboratories and healthcare providers confidence in the results each and every time, ultimately helping to enhance patient management and outcomes.”
XTALKS WEBINAR: Using the Pain Catastrophizing Scale in Clinical Research and Practice
Live and On-Demand: Thursday, June 09, 2022, at 11am EDT (4pm BST/UK)
Register for this free webinar to learn what is currently known about the causes and consequences of pain catastrophizing with particular emphasis on the importance of assessing pain catastrophizing in clinical trials of treatments for persistent pain conditions.
How Does Hologic’s Aptima CMV Test Work?
First, a whole blood or plasma specimen is treated with a detergent that can dissolve the encapsulation of the virus. The detergent will denature the proteins and result in the release of the viral genomic DNA. The developed primers or the capture oligonucleotides will target and bind to the viral DNA and thus, they will form a hybrid called an amplicon.
The assay uses “torches” which are fluorescent signals that will “glow” after binding with the target amplicon. The amount of “glow” is directly proportional to the concentration of CMV in the provided specimen. The effectiveness of the anti-CMV treatment in a patient can be regularly monitored by observing the increase or decrease of the fluorescence.
Hologic — Past, Present and Future
Hologic Inc. is well established in diagnostic and viral load testing by developing assay techniques for HIV-1, Hepatitis C and Hepatitis B. Currently, Hologic is developing other transplant assays for in vitro diagnosis of BK virus and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). The company is anticipating regulatory approvals for these assays.





Join or login to leave a comment
JOIN LOGIN