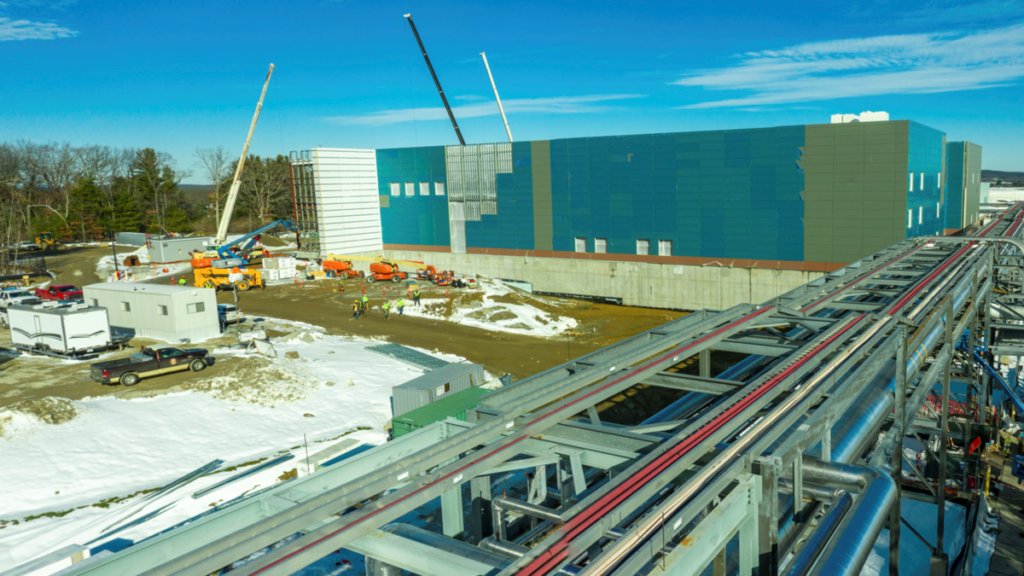
Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), a multinational pharmaceutical company based in New York City, has announced that its new state-of-the-art cell therapy manufacturing facility in Devens, Massachusetts, has received approval for commercial production from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This is BMS’ third commercial CAR T manufacturing facility in the US.
This facility complements BMS’ global network of advanced cell therapy manufacturing sites, which currently includes locations in Bothell, Washington; Warren, New Jersey; and Summit, New Jersey. Additionally, BMS is developing another manufacturing site in Leiden, Netherlands.
The Devens site represents a significant step in BMS’ ongoing efforts to expand its global cell therapy manufacturing capabilities and ensure a stable supply of cell therapies for its portfolio in the long term.
“The Devens facility integrates the latest state-of-the-art technology in the industry with top talent in the Boston area that will take us into the next phase of our cell therapy journey,” said Karin Shanahan, executive vice president, Global Product Development & Supply, BMS, in the company’s press release. “We are working diligently to increase our product capacity through new sites like Devens and by implementing innovative manufacturing solutions that help patients in need.”
The newly built cell therapy manufacturing facility, which covers an impressive 244,000 square feet, represents the second major expansion of BMS’ 89-acre site in Devens. Over the past decade, this site has been pivotal in the development, production and testing of both clinical and commercial medications.
Cell therapy involves introducing new cellular material, either autologous (derived from the patient) or allogeneic (from a donor), into a patient’s body. It serves various purposes, such as replacing diseased or damaged cells, modulating the function of the patient’s cells or eliminating disease-causing or dysfunctional cells using immune cells.
The manufacturing process for cell therapies, like autologous T cell therapy, is complex and labor-intensive, involving numerous procedures that can affect regulatory compliance and consistency. Each batch of engineered T cells is manufactured individually and subsequently infused back into the original patient. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure a reliable, high-quality supply with rapid turnaround time for cell therapy manufacturing.
“Bristol Myers Squibb’s vision of putting more patients on a path to potential cure starts with delivering on the promise of our current product portfolio and future pipeline,” said Lynelle Hoch, senior vice president, Global Cell Therapy Franchise Lead, BMS, in the news release. “Today’s approval underscores our commitment to deliver our transformational CAR T-cell therapies to more patients.”
XTALKS WEBINAR: Revolutionizing Cell and Gene Therapy Trials with Human-Centered Design and Real Patient Narratives
Live and On-Demand: Tuesday, July 18, 2023, at 1pm EDT (10am PDT)
Register for this free webinar to learn about the true potential of study companion apps, redefining the intricate realm of cell and gene therapy trials and fostering meaningful patient experiences in the world of tech-driven research.
Recent FDA Approvals of Cell Therapy Manufacturing Facilities in the US
Successful commercialization of novel cell therapy requires exemplary performance at all stages, including upstream and downstream processing, process development, testing and manufacturing services.
In recent years, several cell therapy manufacturing facilities in the US have garnered FDA approval. A notable instance is Kite, a Gilead Company, a global biopharmaceutical enterprise based in Santa Monica, California. In 2022, Kite reported that their newly established CAR T-cell therapy manufacturing facility in Frederick, Maryland, had received FDA approval for commercial production, marking a significant milestone within Kite’s global manufacturing network for CAR T-cell therapies.
Moreover, Lonza, a global manufacturing partner for the pharmaceutical, biotech and nutrition industries, announced that two cell and gene therapies manufactured at their Houston site got FDA approval in 2022. The recent FDA approvals of Zynteglo (betibeglogene autotemcel) and Skysona (elivaldogene autotemcel), both products of bluebird bio, indicate that Lonza’s Houston site in the US now provides manufacturing services for three commercial cell and gene therapy products, including cell therapy and viral vector manufacturing.
The Global Cell Therapy Market Continues to Expand
The global cell therapy market, valued at $10.35 billion in 2021, is projected to reach an impressive $60.67 billion by 2030. The market anticipates a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.72 percent during the 2022 to 2030 forecast period. This growth is driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, infections and diabetes, along with a surge in research activities and clinical trials in the field of cell therapy, contributing to global market expansion.
In 2021, North America dominated the cell therapy market, accounting for a significant revenue share of 53 percent. This can be attributed to the rising incidence of chronic diseases and considerable investments in cell therapy development, particularly in the US. The use of stem cell technologies to treat various diseases has also catalyzed the growth of the cell therapy market in North America; however, the Asia-Pacific region holds substantial potential for market growth, primarily due to its large population. The Asia-Pacific market is forecasted to experience the highest growth rate of 16 percent during the forecast period, driven by factors such as favorable government regulations, improved healthcare facilities, lower costs and advancements in cell therapy technologies.






Join or login to leave a comment
JOIN LOGIN