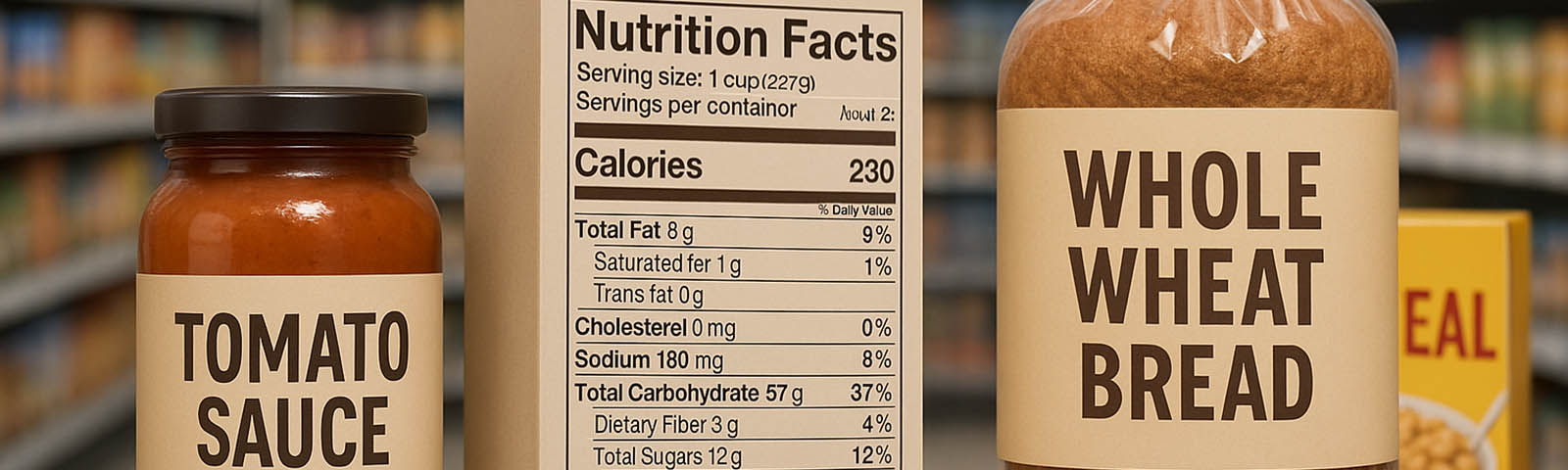
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is set to remove brominated vegetable oil from its list of approved food additives after raising health concerns. This move comes after the FDA National Center for Toxicological Research, the Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition and Toxicologic Pathology Associates in the US uncovered new evidence pointing to brominated vegetable oil’s potential harm.
Originally sanctioned for use in measured doses, brominated vegetable oil has been used to keep citrus flavors from separating in some beverages. Similarly, bromine is widely used in the manufacturing of flame-retardant materials. Now, the FDA’s reevaluation of the oil’s safety profile has led to the consideration of a complete ban.
The reassessment of brominated vegetable oil’s place in the food industry aligns with the FDA’s obligation to base regulatory actions on scientific findings and risk assessments. Subsequent research has verified earlier suspicions about the adverse health impacts linked to the consumption of brominated vegetable oil.
Related: Top 5 Foods Banned in Europe
“The agency concluded that the intended use of [brominated vegetable oil] in food is no longer considered safe after the results of studies conducted in collaboration with the National Institutes of Health [NIH] … found the potential for adverse health effects in humans,” said James Jones, the FDA’s deputy commissioner for human foods, in a statement.
A particularly damning study, recently featured in the journal Food and Chemical Toxicology, connects brominated vegetable oil intake to heightened concentrations of bromine within bodily tissues, with a notable focus on thyroid health implications. This latest study’s rationale for recommending the ban on brominated vegetable oil is compelling.
Researchers observed crucial changes in the thyroid-related markers of rats subjected to brominated vegetable oil in their diet over a 90-day period. High doses correlated with an increase in serum bromide levels, thyroid follicular cell hypertrophy, an uptick in thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and a reduction in thyroxine (T4), especially in male rats.
Further findings showed a distinct dose-response relationship, with increased levels of di- and tetra-bromo stearic acid in the heart, liver and fat tissues. These discoveries solidify the link between brominated vegetable oil exposure and the accumulation of bromine compounds in organs, underscoring the thyroid as a particularly vulnerable target for toxicity.
Despite its infrequent use in beverages today, and even though the regulatory oversight for brominated vegetable oil shifted after it was stripped of its “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS) status in 1970, concerns persist.
In a broader regulatory context, the FDA’s stance on brominated vegetable oil comes after a similar prohibition in California. The FDA’s review encompasses a variety of food-related chemicals, including color additives, ensuring alignment with the safety standards that led to California’s earlier decision.
Additionally, the FDA is currently revamping its Human Foods Program (HFP) to enhance the safety evaluation of food chemicals. Central to this revamp is the proposed Office of Food Chemical Safety, Dietary Supplements and Innovation, aimed at creating a more effective and flexible review process for substances in the food supply, prioritizing timely and dynamic assessments.
This regulatory shift echoes international concerns. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also sought public feedback on its draft opinion concerning polybrominated diphenyl ethers. These brominated flame retardants, often found in animal-derived foods, are under scrutiny for their potential to cause reproductive and nervous system harm, reflecting a growing global caution around the use of brominated compounds in food products.










Join or login to leave a comment
JOIN LOGIN