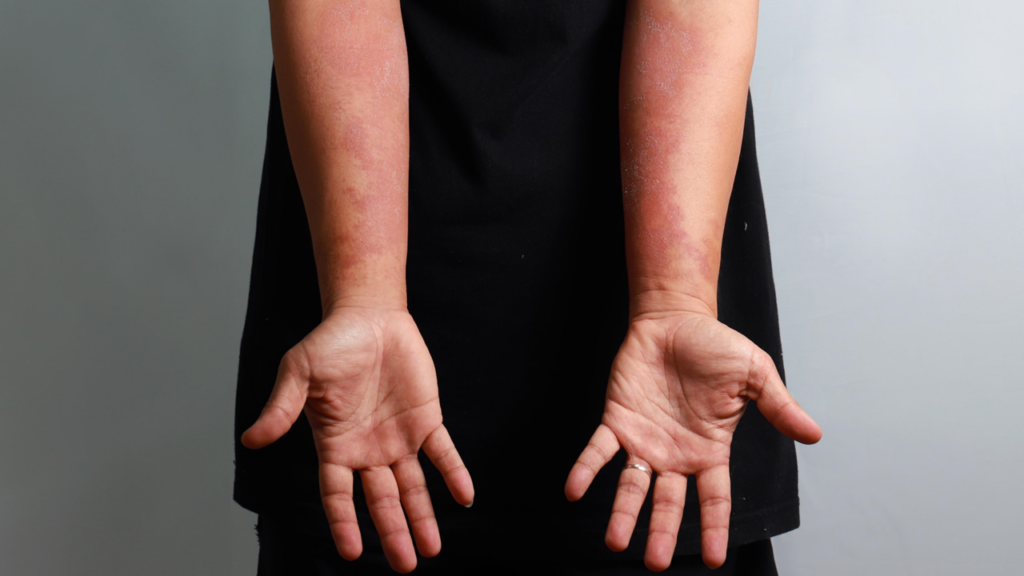
Promising new data from UNION Therapeutics’ ADESOS Phase IIb study show orismilast’s potential as an effective oral treatment for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.
Presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress 2024, the study highlighted significant improvements in key disease markers, positioning orismilast as a potential breakthrough in atopic dermatitis management.
UNION now plans to advance orismilast to a Phase III trial, pending US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of the trial design.
Studies show that PDE4 inhibitors work by increasing cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels in immune cells, which suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, interleukins and IFN-γ. This leads to broad anti-inflammatory effects, benefiting conditions like atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Orismilast specifically targets the PDE4B/D subtypes linked to inflammation, acting early in the cascade to inhibit Th1, Th2 and Th17 pathways.
XTALKS WEBINAR: Optimizing Clinical Trial Protocols: How Digitized Protocols are Accelerating Clinical Research
Live and On-Demand: Monday, November 4, 2024, at 12pm EST (5pm GMT/UK)
Register for this free webinar to gain insights into protocol digitization, understand how it can drive efficiencies and discover how it can elevate clinical trials.
The ADESOS Phase IIb study enrolled 233 patients, randomized into three active dose groups (20 mg, 30 mg and 40 mg) and a placebo group. Results showed that significantly more patients in the orismilast groups achieved an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0/1 at Week 16 compared to placebo (26.3 percent, 24.3 percent, 30.9 percent and 9.5 percent, respectively; all p-values <0.05). A notable reduction in the biomarker TARC (CCL17/thymus and activation-regulated chemokine) was also observed, with end-of-treatment levels approaching those of non-lesional skin.
The mean percentage changes in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) at Week 16 were -55.1 percent, -52.2 percent and -61.4 percent for the 20 mg, 30 mg and 40 mg groups, respectively. In patients with more severe disease at baseline (EASI >21), orismilast showed clearer separation from placebo on EASI and other endpoints. Additionally, a rapid onset of action was observed, with significant reductions in itch Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) scores by Week 2.
Safety and tolerability were consistent with previous studies and the PDE4 inhibitor class, with the most common side effects being mild diarrhea, nausea and headache, mainly occurring within the first month.
Related: Ebglyss (Lebrikizumab) Approved for Atopic Dermatitis, Offering Early Itch Relief
Orismilast is also being investigated for other conditions, including psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa and ulcerative colitis.
Following a positive End-of-Phase II meeting with the FDA and a Fast Track designation, UNION is set to proceed with Phase III development.
EADV 2024 also featured other clinical trial data aimed at addressing the complexities of atopic dermatitis. Galderma shared new data on nemolizumab, highlighting its long-term efficacy and safety over a 68-week treatment period and its potential to significantly reduce itch and skin lesions in atopic dermatitis patients. Additionally, LEO Pharma continues to present new data on tralokinumab, showcasing advancements in treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in several difficult-to-treat regions.
Efforts to better understand the real-world impact of atopic dermatitis are also underway. Recently, Thermo Fisher Scientific launched the CorEvitas Clinical Registry to collect data on disease progression and treatment outcomes in adolescents.
Meanwhile, Astria Therapeutics’ drug, STAR-0215, which has received Orphan Drug designation for hereditary angioedema, is also being studied in preclinical trials for atopic dermatitis, further expanding the research landscape for potential long-term treatment solutions.





Join or login to leave a comment
JOIN LOGIN