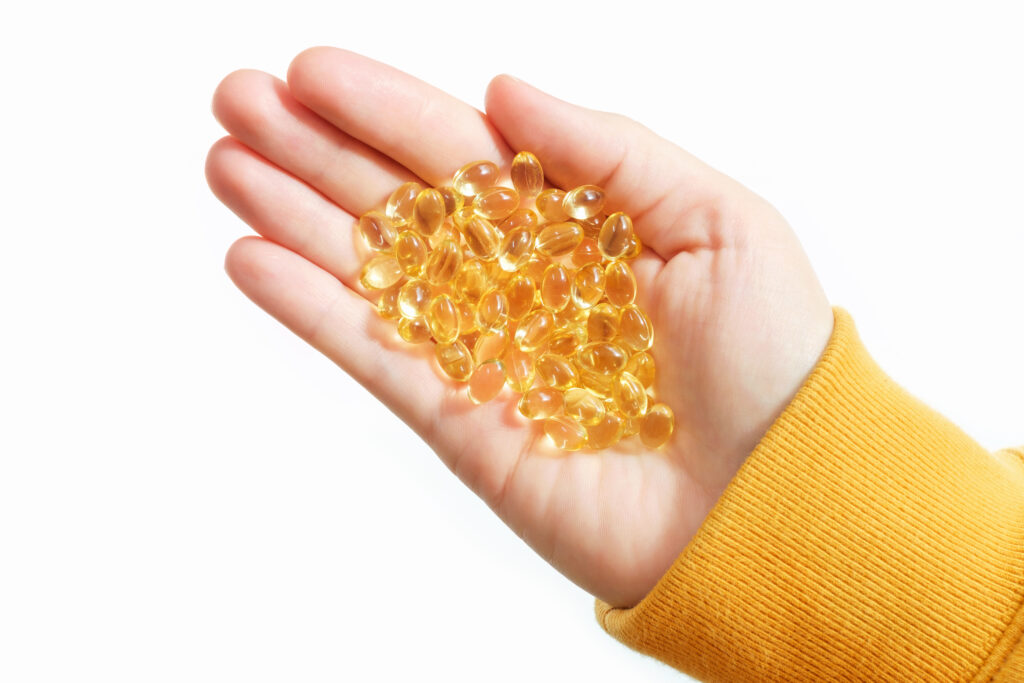
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) recently released a technical report that shed light on eight emerging food safety risks, including vitamin D overdose. The report was a culmination of collaborations involving the Emerging Risks Exchange Network (EREN), the Stakeholder Discussion Group on Emerging Risks, EFSA’s diverse scientific bodies and its numerous working groups.
Throughout 2021, a total of 18 potential threats were deliberated upon. Of these, eight were recognized as emerging risks. The classifications for these issues were primarily based on the identified hazards or drivers. In four of the issues discussed in 2021, a change in consumer trends was identified as a driver. Four were classified as chemical hazards and six were identified as microbiological hazards.
The emerging food safety risks include:
- Vitamin D overdose risks stemming from food supplements;
- A novel ovine pest virus, showing similarities to the classical swine fever virus, discovered in Italy;
- The first-ever identification of West Caucasian Lyssavirus in Italy;
- The surfacing of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia albertii (STEA);
- Probable health repercussions from coconut oil consumption, including the risk of elevated LDL-cholesterol levels and potential induction of insulin resistance;
- Prospective risks linked to the declining usage of pesticides and fertilizers in food crops, leading to possible deterioration in food quality and safety due to heightened presence of harmful organisms;
- The detection of brevetoxins in French shellfish; and
- Mycoplasma bovis infections, primarily observed in Belgium.
Related: Skittles Ban? California Passes Landmark Food Safety Bill
Delving deeper into the vitamin D overdose risk, in 2019 and 2020, at least 23 overdose incidents related to children’s vitamin D supplements prompted calls to Poison Control Centers. In 2020, the Environmental and Occupational Health and Safety recorded two severe instances of vitamin D overdose in infants due to supplements purchased online. By 2021, a pediatric hospital reported a case of severe hypercalcemia. Nations were encouraged to consult with national pediatricians to determine if there was a rising trend of vitamin D overdoses in infants.
Discussion also revolved around STEA, a species of bacterium in the same family as E. coli. The primary source of STEA remains uncertain, but pinpointing it is crucial for understanding transmission patterns and mitigating infections. Nations were prompted to gather data regarding incidence, human prevalence and risk exposure channels to more comprehensively define the threat.
Concerns about the potential health implications of coconut oil consumption were raised. Specialists emphasized the need for more comprehensive research to solidify the evidence concerning its possible toxicity. Countries were advised to review their national statistics to verify if there was an ascending trend in the dietary intake of coconut oil.
The presence of brevetoxins in French shellfish was also highlighted. Recognized as marine biotoxins, they are culpable for neurotoxic shellfish poisoning upon ingestion of tainted shellfish. These toxins currently have no regulatory framework in Europe, and experts advised monitoring brevetoxins in European marine environments.
Furthermore, the report listed an additional 35 potential risks, identified by EREN members representing a range of global food safety organizations including the World Health Organization (WHO) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Some other intriguing topics included the surging consumption of crocodile meat, contamination of meat due to perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) hotspots, presence of synthetic cannabinoids in food and potential food fraud concerning buffalo milk, among others.










Join or login to leave a comment
JOIN LOGIN