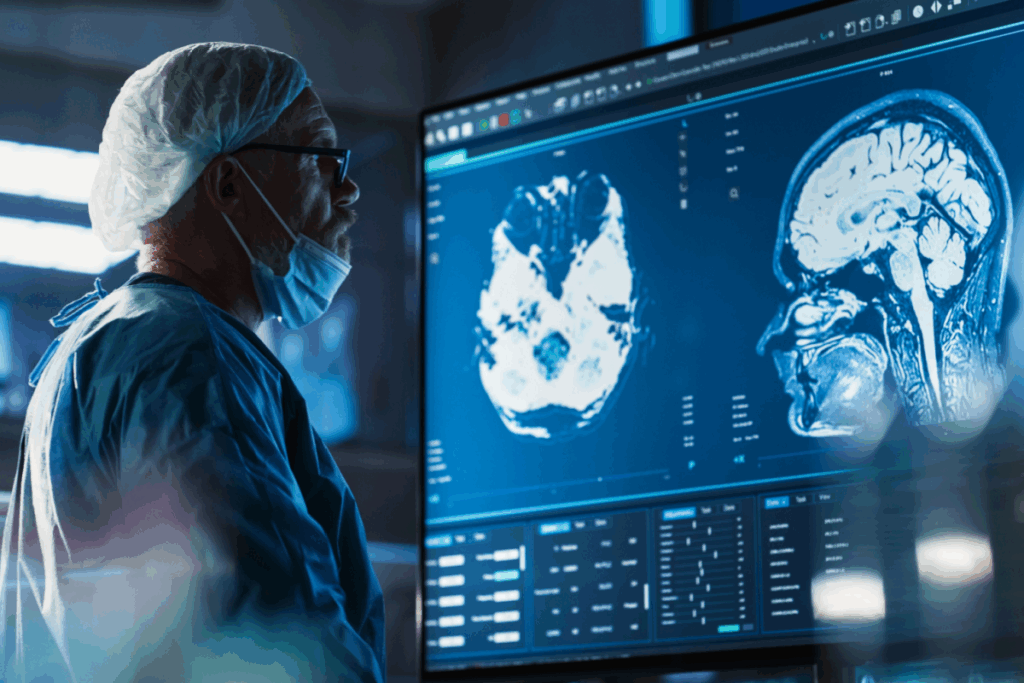
The FDA has cleared Canadian medical device company mlHealth 360’s Scaida BrainCT-ICH, an AI software device designed to triage suspected intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) on non-contrast head CT scans. The 510(k) clearance (K250694) authorizes clinical use in US hospital settings and marks the first time a Canadian-developed AI system for ICH triage has been cleared by the agency.
ICH involves bleeding inside the skull that can quickly damage brain tissue, making rapid review of CT scans crucial. Emergency departments are seeing record imaging volumes, which can leave time-sensitive studies waiting in a backlog during peak hours.
AI is becoming more common in radiology as imaging volumes go up and hospital teams manage increasing operational pressures. Deep learning systems are being researched to support tasks where automation can help standardize workflows and reduce delays without replacing clinical judgment.
Scaida BrainCT-ICH is an AI-powered workflow triage tool that analyzes head CT scans immediately after acquisition. Triage AI does not diagnose a condition; instead, it moves suspected urgent cases to the top of a radiologist’s queue so they can be reviewed sooner. The software processes each scan in about six seconds, allowing it to flag urgent findings without slowing routine workflow, and it does not modify images or provide a diagnostic conclusion.
According to the company, the software is designed to ease operational strain in radiology departments by helping radiologists reach urgent cases sooner.
The system fits into existing PACS and RIS workflows (the imaging and reporting systems used in radiology) and processes each scan in an average of 5.97 seconds. A specificity of 0.887 indicates fewer false alarms, helping reduce alert fatigue, and a sensitivity of 0.867 reflects how often the system correctly flags scans that may contain a hemorrhage.
The FDA’s decision is supported by validation data from six US institutions using scanners from GE, Toshiba and Siemens across varied patient populations. Reported performance metrics include a sensitivity of 0.867, a specificity of 0.887 and an area under the curve of 0.926.
Scaida BrainCT-ICH is cleared for use by trained radiologists as an assistive tool to prioritize suspected ICH cases.
Executives in the press release also referenced future development plans in additional imaging domains, though no specific regulatory pathways or timelines were detailed. The company has not announced US launch timing or additional regulatory submissions.
XTALKS WEBINAR: Medical Device Validation Solutions for Evolving Industry Needs
Live and On-Demand: Wednesday, January 21, 2026, at 1pm EST (10am PST)
Register for this free webinar to learn why Computer Software Assurance (CSA) demands a rethink of traditional validation for medical devices.
Other New Neuroimaging AI Advances in 2025
In 2025, several neuroimaging AI systems moved through FDA review or entered US clinical workflows.
Methinks AI received two FDA clearances for its non-contrast CT and CT angiography (CTA) stroke modules, which detect suspected large vessel occlusions and ICH on non-contrast and angiographic CT scans, including distal occlusions up to the MCA-M2 segment.
RapidAI expanded its portfolio with five FDA-cleared modules for suspected midline shift, obstructive hydrocephalus, large and distal vessel occlusions and automated alignment of serial CT scans to help clinicians track subtle intracranial changes over time.
Qure.ai was FDA-cleared for qER-CTA, which analyzes CTA for suspected large vessel occlusions in the internal carotid artery and MCA-M1 territories to support faster triage and specialist notification.
Brainomix advanced its FDA-cleared 360 Stroke platform with CT-based tools that estimate ischemic core volume to inform early treatment and transfer decisions.
Outside of emergency CT pathways, Philips and Cortechs.ai extended their partnership to bring quantitative magnetic resonance capabilities directly into Philips MR workflows. These include brain volumetrics, lesion burden analysis and tumor tracking to support more consistent assessment of neurodegenerative and neuro-oncology conditions.
Overall, these developments demonstrate how AI applied across CT, CTA and magnetic resonance imaging can help radiology teams manage workload and identify urgent or evolving neurological findings earlier in the care pathway.
If you want your company to be featured on Xtalks.com, please email [email protected].











Join or login to leave a comment
JOIN LOGIN