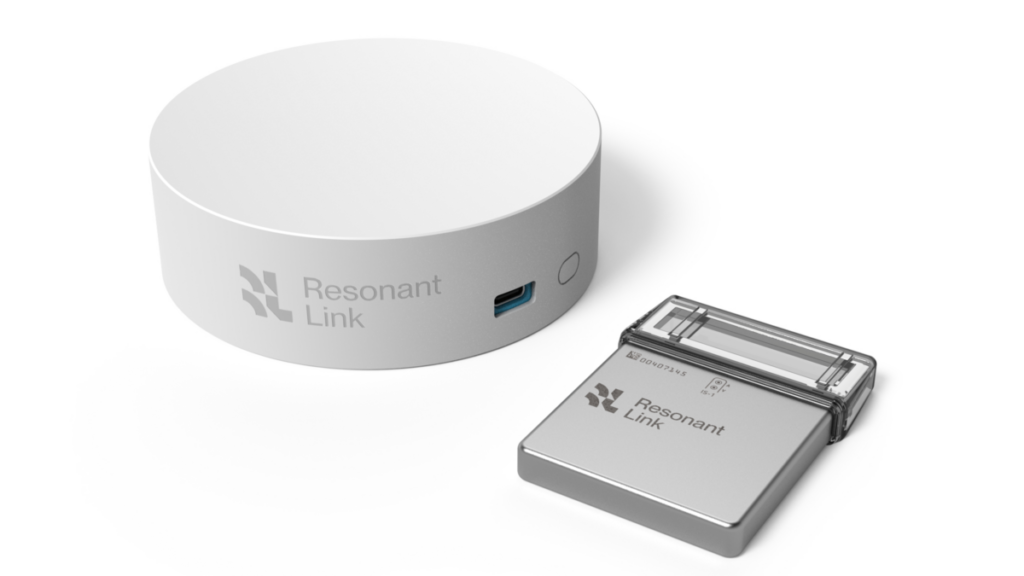
Resonant Link, a wireless charging technology company headquartered in Vermont, recently revealed their latest and the world’s fastest charger for titanium can-based medical device implants. With a three times faster charging speed, patients can complete charging in 15 minutes while going about their daily lives, instead of having to sit still for up to hours every week while their implantable device is charging.
“Customers who’ve had a sneak peek at our ti-can platform have been blown away by its speed and spatial freedom, giving patients freedom to live their lives with these critical treatments,” said Aaron Stein, Resonant Link’s CTO, in the company’s news release.
Before wireless charging, medical implant batteries were either replaced with surgery or recharged with a driveline, a wire that is permanently installed on a patient’s stomach and connects the device to a battery outside the body. Both methods are invasive and have various disadvantages, including:
- Difficulty in implanting bulky battery packs in compact areas (e.g., the brain)
- Increased risks of infection, wire dislodgement and fracture
- Battery replacement surgery as often as every few years, adding to mortality risk and billions in healthcare costs
To circumvent the inherent drawbacks of the existing procedures, Resonant Link is promoting their wireless charger as a safe, non-invasive alternative. The wireless charger — the transmitter — contains a metallic coil that converts electrical energy into a magnetic field, which is then collected and reverted into electricity by the receiver inside the implanted device. Resonant Link’s patented multi-layer, self-resonant structure (MSRS) coils can charge devices more quickly and efficiently than currently available technologies.
“Our wireless charging platform for titanium-can-based implants is a direct result of listening to patients,” said Grayson Zulauf, Resonant Link’s CEO, in the company’s press release. “Current wireless chargers are slow to recharge implants and incredibly difficult to align, making recharging the single most common patient complaint for many active implantable devices, like spinal cord stimulators. Our wireless charging for titanium cans changes all of that.”
XTALKS WEBINAR: Drug Delivery — Addressing Global Regulatory Challenges in Co-Packaged, On-Body Systems
Live and On-Demand: Thursday, June 15, 2023, at 10am EDT (4pm CEST/EU-Central)
Register for this free webinar to learn about the differences and similarities between the US and EU regulatory frameworks for co-packaged combination products. The featured speakers will discuss how device and drug manufacturers can work cohesively to address the regulatory requirements in both the US and EU markets.
Resonant Link Set to Capitalize on a Booming Medical Implants Market
Microelectronic medical implants had a market size of $43.4 billion in 2022. This figure is expected to more than double and reach $98.5 billion by 2032. A major factor driving this demand is the growing elderly population, along with the rising cases of diseases such as epilepsy, cardiovascular diseases and Parkinson’s disease.
With a $9.3 million seed round raised in early 2022, Resonant Link has partnered with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in the medical device industry and offers several charging platforms and, upon request, full charger customization.
Resonant Link’s criteria for customized charger configuration include size, implant depth, power level, output voltage, battery type and integration. The currently applicable devices for Resonant Link’s wireless chargers include neurostimulators (deep brain, sacral nerve, spinal cord), implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), pacemakers, neural implants, intrathecal pain pumps, total artificial hearts (TAHs) and ventricular assist devices (VADs).
In addition, Resonant Link can charge implants that are as small as 3 mm in diameter and implanted up to 6 cm deep, all while meeting the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-mandated temperature limits for implants that prevent surrounding tissues from burning.
Resonant Link’s medical device chargers are undergoing animal trials this year. Zulauf expects human trials and the first FDA approval as early as 2024.










Join or login to leave a comment
JOIN LOGIN