Philips has initiated a recall and discontinued the distribution of its Tack endovascular system after reports surfaced that users experienced challenges during procedures. The FDA classified this recall as the most serious type of recall (Class I), urging healthcare facilities to immediately halt use of the product.
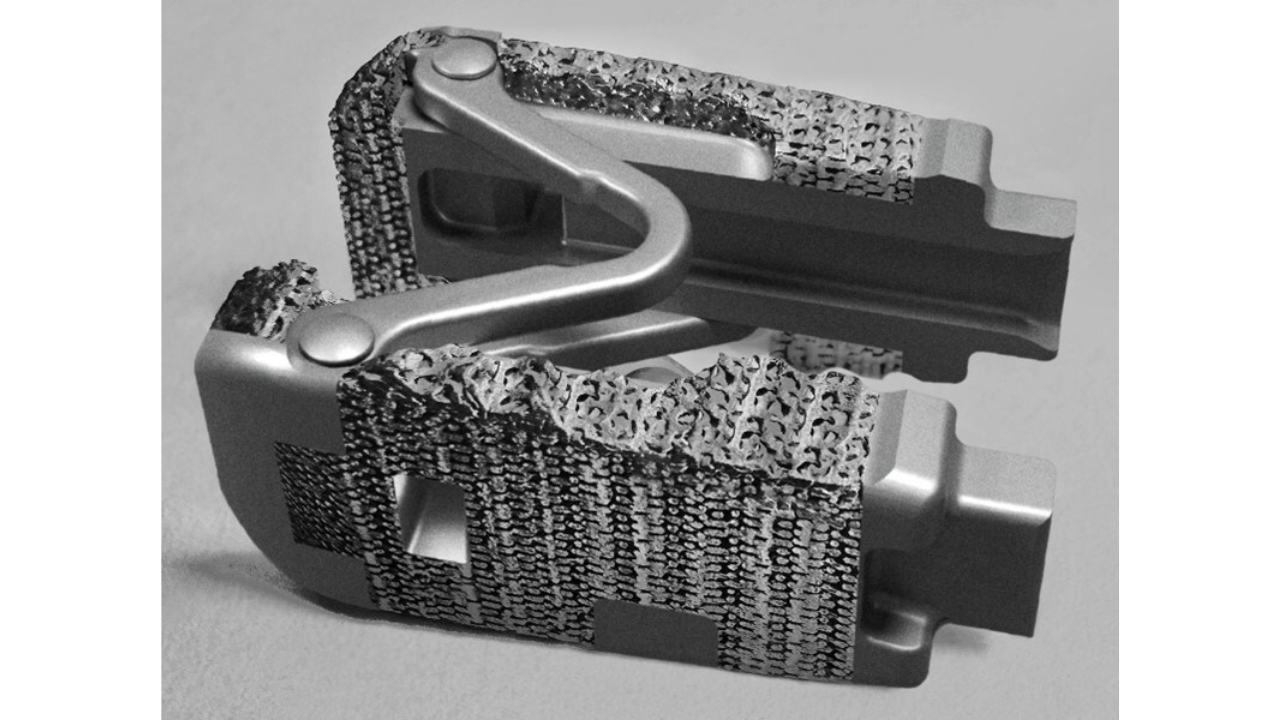
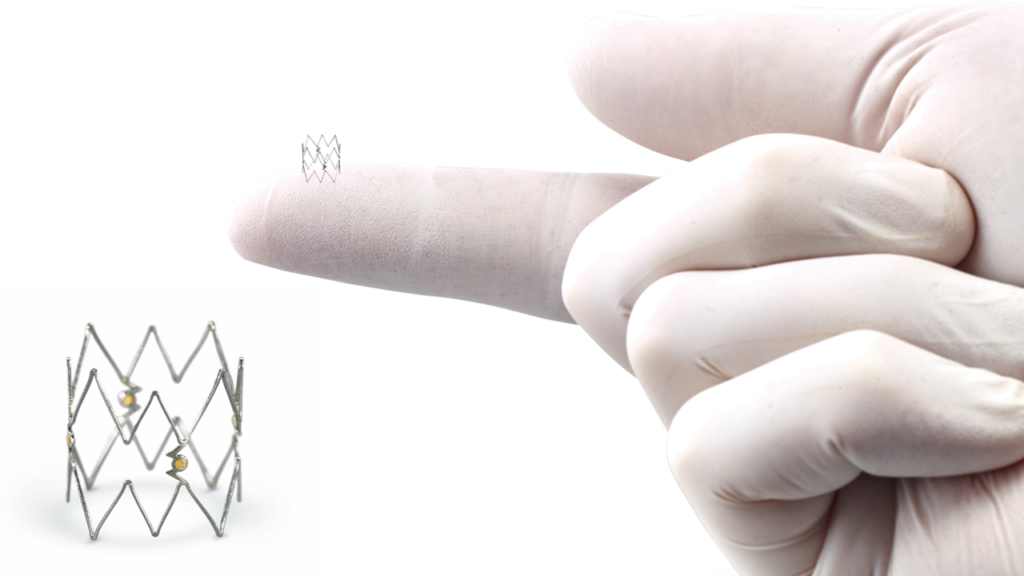
Designed to treat blood vessel dissection — a condition that can occur when arteries are widened during angioplasty (a procedure that uses a balloon or stent to open narrowed arteries) — the Tack endovascular system deploys small implants to reattach the damaged inner lining of the vessel, much like a safety clip holds pages together.
Developed as part of Philips’ strategic expansion into image-guided therapy through its 2020 acquisition of Intact Vascular, the system has shown promising efficacy.
A 2022 study — the Tack Optimized Balloon Angioplasty (TOBA) II below-the-knee (BTK) trial — demonstrated that the Tack endovascular system (4F) achieved a 93.9% target limb salvage rate and 69.6% freedom from clinically driven target lesion revascularization at three years, underscoring its role in treating BTK arterial dissections in patients with critical limb ischemia.
However, practitioners have reported that additional interventions were sometimes required to reposition or remove the implant, posing significant health risks. Affected products include several sizes and configurations, each marked with specific unique device identifiers and batch codes.
The impacted products are as follows:
- Tack endovascular system (4F, 1.5 to 4.5mm), 150cm
- Tack endovascular system (6F, 3.5 to 6.0mm), 135cm
- Tack endovascular system (6F, 4.0 to 8.0mm), 135cm
The “F” stands for French gauge — a standard measurement for the diameter of medical devices where one French is about 0.33 mm.
Philips Image Guided Therapy Services communicated urgent instructions on January 10, 2025, requiring customers to check inventories, quarantine affected devices and complete a response form within seven days.
The recall comes amid growing concerns over adverse effects such as occlusion (blockage of blood flow), dissection (tears in the arterial wall) and perforation, which can lead to complications including pain, tissue loss, restenosis, bypass surgery or even amputation.
To date, 20 injuries have been reported, though no deaths have been attributed to the device.
This recall is one chapter in a series of safety measures Philips has implemented in recent years.
In past FDA news releases, the company addressed issues like the degradation of sound abatement foam in its sleep therapy devices — which could result in the inhalation of foam particles — and updated instructions for continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) masks with magnetic headgear clips to avoid interference with implanted devices.
More recently, revised usage guidelines for Trilogy Evo ventilators were issued to counter potential inaccuracies caused by aerosol deposits on flow sensors.
Notably, in 2024, two other companies issued recalls on devices in related categories: Sleepnet Corporation initiated a worldwide recall of CPAP and BiPAP masks with magnets due to potential interference with implanted devices, and Baxter issued an urgent recall for its Volara system single-patient use circuit.









Join or login to leave a comment
JOIN LOGIN